All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Typically, these conditions apply: Proprietors can select one or several recipients and define the percentage or repaired amount each will certainly obtain. Recipients can be individuals or organizations, such as charities, however different rules make an application for each (see listed below). Owners can alter beneficiaries at any kind of point throughout the contract duration. Proprietors can choose contingent beneficiaries in case a prospective successor dies prior to the annuitant.
If a wedded pair possesses an annuity jointly and one partner dies, the enduring spouse would certainly proceed to get payments according to the terms of the contract. To put it simply, the annuity remains to pay as long as one partner lives. These contracts, in some cases called annuities, can additionally include a third annuitant (typically a child of the pair), that can be designated to get a minimum variety of settlements if both partners in the initial agreement pass away early.
How is an inherited Annuity Rates taxed
Here's something to keep in mind: If an annuity is sponsored by an employer, that business must make the joint and survivor plan automatic for couples who are wed when retired life happens., which will certainly affect your month-to-month payment in a different way: In this instance, the monthly annuity repayment stays the very same adhering to the fatality of one joint annuitant.
This type of annuity might have been bought if: The survivor intended to handle the financial responsibilities of the deceased. A pair handled those responsibilities with each other, and the enduring partner wants to avoid downsizing. The surviving annuitant obtains just half (50%) of the regular monthly payout made to the joint annuitants while both were to life.
Do beneficiaries pay taxes on inherited Annuity Beneficiary
Many agreements enable a making it through spouse provided as an annuitant's recipient to transform the annuity right into their very own name and take over the initial agreement., who is qualified to receive the annuity only if the key recipient is incapable or reluctant to accept it.
Squandering a round figure will set off differing tax obligation liabilities, depending on the nature of the funds in the annuity (pretax or already exhausted). Tax obligations won't be incurred if the spouse proceeds to get the annuity or rolls the funds right into an Individual retirement account. It might seem odd to assign a minor as the recipient of an annuity, but there can be excellent reasons for doing so.
In other situations, a fixed-period annuity may be utilized as a lorry to fund a child or grandchild's university education. Annuity income riders. There's a distinction in between a trust fund and an annuity: Any type of money appointed to a depend on has to be paid out within 5 years and does not have the tax obligation advantages of an annuity.
A nonspouse can not commonly take over an annuity contract. One exemption is "survivor annuities," which supply for that backup from the beginning of the contract.
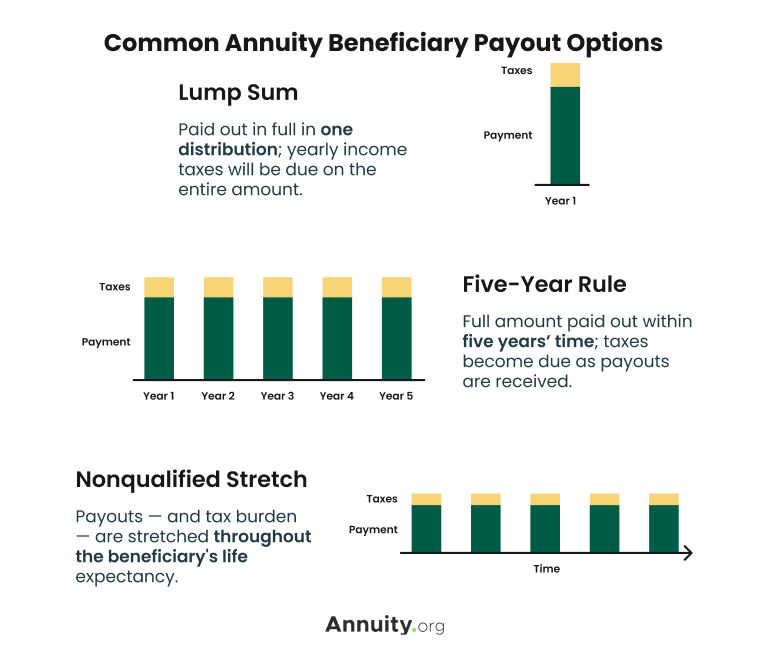
Under the "five-year rule," recipients might delay claiming money for up to 5 years or spread payments out over that time, as long as all of the cash is collected by the end of the fifth year. This enables them to expand the tax obligation problem gradually and may maintain them out of greater tax obligation braces in any type of single year.
As soon as an annuitant dies, a nonspousal beneficiary has one year to establish a stretch circulation. (nonqualified stretch arrangement) This layout establishes up a stream of revenue for the remainder of the recipient's life. Since this is established up over a longer duration, the tax implications are typically the tiniest of all the choices.
Tax implications of inheriting a Annuity Cash Value
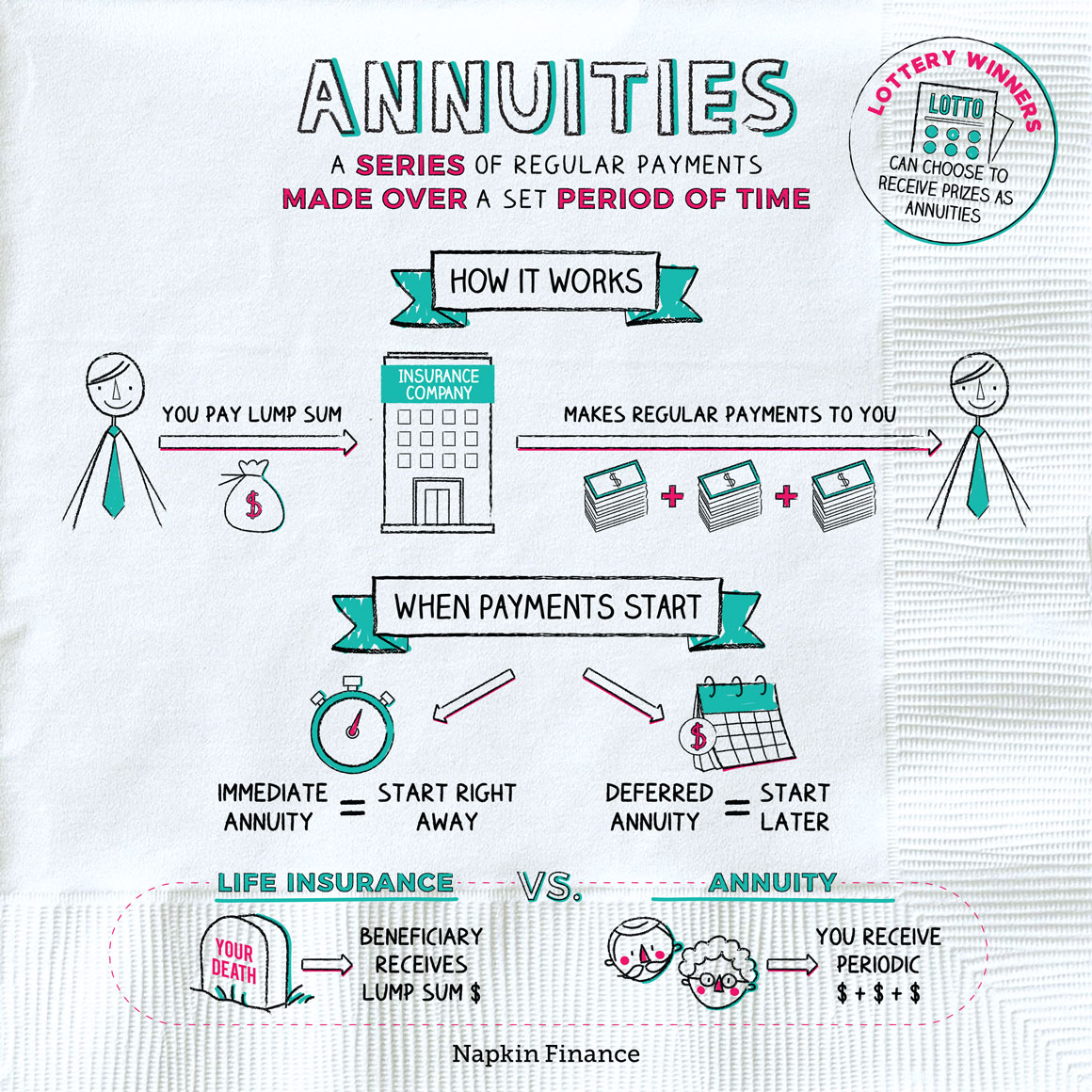
This is occasionally the case with immediate annuities which can begin paying out right away after a lump-sum investment without a term certain.: Estates, depends on, or charities that are beneficiaries should take out the agreement's amount within five years of the annuitant's fatality. Tax obligations are influenced by whether the annuity was moneyed with pre-tax or after-tax dollars.
This merely implies that the cash purchased the annuity the principal has actually currently been tired, so it's nonqualified for tax obligations, and you don't need to pay the internal revenue service once again. Just the interest you gain is taxable. On the other hand, the principal in a annuity hasn't been exhausted.
When you withdraw cash from a certified annuity, you'll have to pay taxes on both the rate of interest and the principal. Profits from an inherited annuity are dealt with as by the Irs. Gross earnings is income from all sources that are not specifically tax-exempt. But it's not the same as, which is what the IRS makes use of to determine just how much you'll pay.
If you acquire an annuity, you'll have to pay revenue tax on the distinction between the primary paid into the annuity and the value of the annuity when the owner passes away. As an example, if the owner acquired an annuity for $100,000 and made $20,000 in passion, you (the beneficiary) would certainly pay taxes on that particular $20,000.
Lump-sum payouts are exhausted at one time. This alternative has the most serious tax obligation consequences, because your earnings for a single year will be much higher, and you might end up being pressed into a greater tax bracket for that year. Steady repayments are tired as revenue in the year they are received.

Just how long? The ordinary time is concerning 24 months, although smaller estates can be disposed of quicker (often in as low as 6 months), and probate can be even much longer for more complicated situations. Having a valid will can speed up the process, but it can still get slowed down if beneficiaries challenge it or the court has to rule on who should provide the estate.
Tax implications of inheriting a Annuity Rates
Due to the fact that the individual is named in the contract itself, there's nothing to competition at a court hearing. It is essential that a specific person be called as recipient, instead of simply "the estate." If the estate is named, courts will analyze the will to sort points out, leaving the will certainly open to being disputed.
This may deserve taking into consideration if there are reputable fret about the individual called as beneficiary diing before the annuitant. Without a contingent beneficiary, the annuity would likely then become based on probate once the annuitant dies. Speak with a financial consultant about the prospective benefits of calling a contingent beneficiary.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Understanding Financial Strategies A Closer Look at Fixed Annuity Vs Equity-linked Variable Annuity Defining the Right Financial Strategy Features of Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Why Variable Ann
Analyzing Indexed Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity A Comprehensive Guide to Fixed Annuity Vs Equity-linked Variable Annuity Defining the Right Financial Strategy Advantages and Disadvantages of Variable Annui
Exploring the Basics of Retirement Options A Closer Look at Pros And Cons Of Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity Breaking Down the Basics of Investment Plans Benefits of Choosing the Right Financial Pl
More
Latest Posts